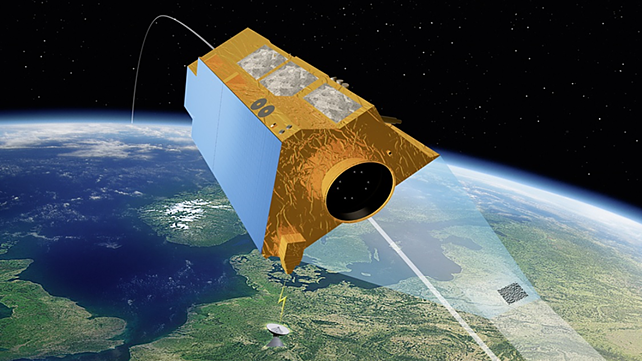
The Airbus-built 'SARah-1' earth observation satellite, under subcontract to OHB System AG, has been transported from Friedrichshafen, Germany, to Vandenberg, California, USA, for its planned launch this month and subsequent operation by Airbus in space.
The satellite, built by Airbus, weighs around four tonne and will be launched from Vandenberg, a press release from the company said.
Airbus' control centre will supervise the launch and commissioning (LEOP) of the satellite in Friedrichshafen. The subsequent calibration, validation and operation will be carried out from the Bundeswehr control centre, the release added.
The overall responsibility for the complete SARah system lies with OHB System AG, Bremen, as the prime contractor, which holds the main contract from the Federal Office of Bundeswehr Equipment, Information Technology and In-Service Support (BAAINBw).
SARah, the replacement for the SAR-Lupe system, is a new operational reconnaissance system consisting of several satellites and a ground segment, which was developed on behalf of the German Bundeswehr.
The architecture of the overall SARah system consists of a space segment with three radar satellites (2 x OHB, 1 x Airbus) and a ground segment connected to two ground stations.
Airbus Defence and Space in Friedrichshafen developed the satellite with the latest, highest-resolution radar technology and jointly developed the ground segment to operate its satellite.
Further, the company has developed the radar instrument featuring a sophisticated, active phased array antenna and represents a further development of the Airbus-built TerraSAR, TanDEM-X and PAZ Earth observation satellites already successfully operating in orbit.
This technology offers the advantages of very fast pointing and very flexible shaping of the antenna beam to deliver imagery in record time, the company added.