Electric two-wheelers (E2Ws) are rapidly gaining traction, particularly in Asian countries, where they are a popular mode of personal transport.
According to a report 'Fire Protection Materials for EV Batteries 2025-2035: Markets, Trends, and Forecasts,' by IDTechEx, 17% of two-wheeler sales in 2023 were electric. As this segment continues to grow, so does the importance of addressing safety concerns, particularly those related to battery fires and thermal runaway.
According to Dr. James Edmondson, VP of Research at IDTechEx and the author of the report, while significant progress has been made in fire protection within the automotive sector, E2Ws present unique challenges in terms of usage, design, and safety regulations, making fire protection materials for E2W batteries a critical focus area.
The Design Differences Between E2W, Electric Car Batteries
The most apparent difference between the batteries of electric cars and E2Ws lies in their size. E2Ws typically use batteries smaller than 4kWh, compared to electric car batteries, which average around 60kWh.
While smaller batteries may pose a less severe fire risk, several kilowatt-hours of energy is still enough to cause significant safety hazards, especially if the fire spreads. A key concern is that many E2W owners charge their vehicles indoors, unlike cars that are often parked outdoors or in garages, which has resulted in fatal incidents in the past.
The growing concern over safety in the E2W market is highlighted by recent incidents, particularly in India. In 2022, a series of fire-related incidents and recalls prompted the Indian government to revise safety standards for E2Ws. These changes, effective from October 1, 2022, include the introduction of a thermal runaway propagation test, requirements for warning systems upon thermal events, and mandatory cell certifications by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). China’s regulations, such as the GB standards, also mandate a delay between a thermal event and visible smoke or fire, aiming to mitigate the spread of fires, Dr Edmondson pointed out.
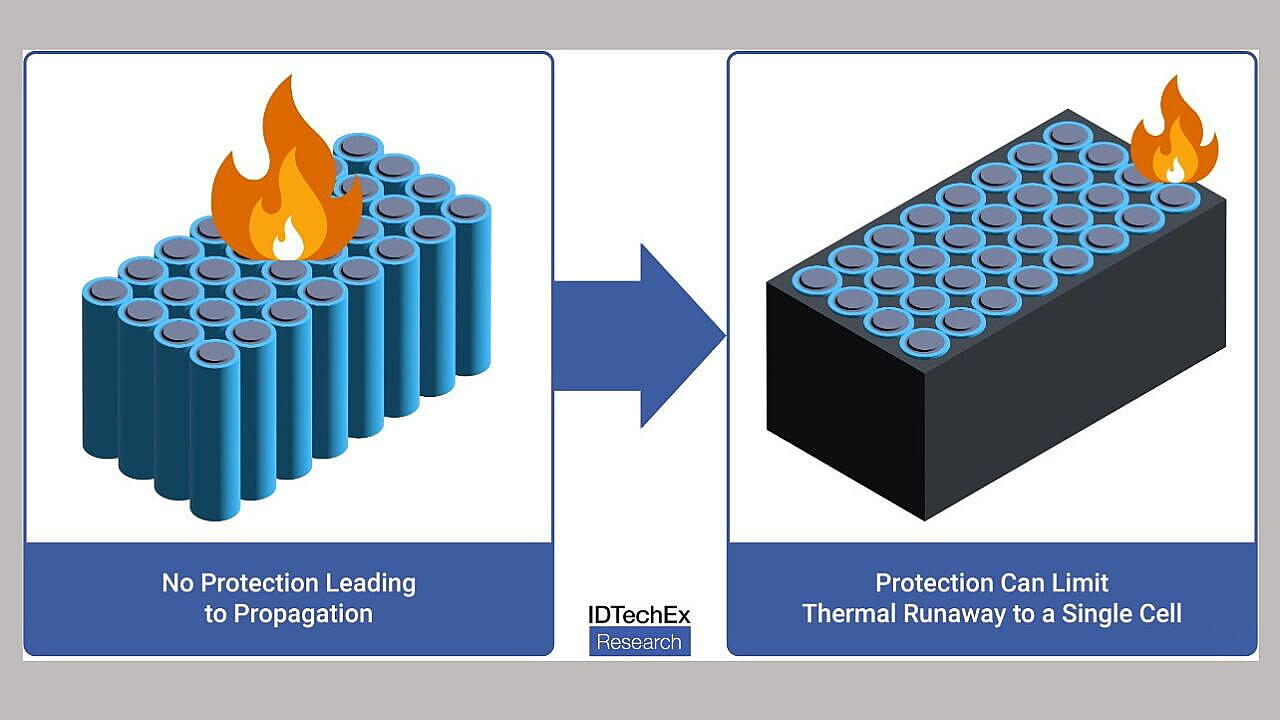
The Role Of Fire Protection Materials In E2W Batteries
As safety regulations in the E2W sector evolve, battery pack designers are being forced to adopt new materials to prevent or delay the propagation of thermal runaway. Cylindrical cells, particularly the 18650 format, are commonly used in E2Ws, and their geometry plays a significant role in determining the materials used for protection. These cells are not as easily stacked as prismatic cells, requiring encapsulation or cell holders to maintain structure and prevent thermal spread.
In the early stages of market development, encapsulants such as thermally conductive foams were used to either spread heat or prevent it from transferring between cells. However, with the introduction of new safety standards, more advanced materials are being developed.
Polymer cell holders with fire-resistant properties are now emerging as a popular solution. These holders, often injection-moulded, provide structure to the battery pack while maintaining cell spacing and preventing thermal runaway propagation. Some of these polymers incorporate glass fibres for enhanced structural performance and even include intumescent properties, expanding and forming a protective barrier when exposed to heat.
Another innovative material gaining traction in E2W battery packs is Phase Change Materials (PCMs). These materials absorb excess heat during phase transitions, typically from solid to liquid. However, they need to be carefully formulated to ensure their structural integrity does not degrade during the phase transition, maintaining their fire protective properties after melting.
In addition to materials that protect individual cells, the choice of polymer for encasing the entire battery pack is crucial. The casing must provide fire protection and impact resistance, particularly in the event of a crash. The combination of these materials is essential for ensuring the overall safety of the battery pack in an E2W Dr Edmondson noted.
Regulatory Impact & Industry Outlook
As with the electric car market, fire safety is becoming a central focus in the E2W sector. While the overall rate of electric vehicle fires remains low, the potential for devastation, particularly in confined spaces, underscores the need for robust safety protocols. Regulations have begun to take shape in regions such as India and China, but it is expected that these will become more stringent over time and expand to other regions as well.
To meet these evolving safety standards, manufacturers are increasingly turning to advanced materials specifically designed for the E2W market. These materials not only help prevent or delay thermal runaway but also support efficient integration into smaller battery packs without compromising performance. As the demand for electric two-wheelers continues to rise, the importance of fire safety will only increase, driving further innovation in materials and technology.
In summary, the E2W market’s focus on fire safety is inextricably linked to the adoption of new materials and regulatory standards. The development of advanced fire protection solutions, including polymer cell holders, Phase Change Materials, and improved battery casings, will continue to play a pivotal role in the safety and growth of the electric two-wheeler market. With increasing regulations and technological advancements, the E2W industry is set to see continued progress in making electric two-wheelers safer for users worldwide, Dr Edmondson added.
Also Read:
How BGauss Blends Innovation, Precision Engg For Sustainable E2W Manufacturing

